Tutorial
How RequestPolicy Works
Every time a web page tells Firefox to make a request to a different website, Firefox asks RequestPolicy whether the request should be allowed. To decide whether to allow the request, RequestPolicy looks for rules in three places:
- Your policy: rules you have created in RequestPolicy.
- Subscription policies: rules maintained by the RequestPolicy developers.
- Default policy: the rule to use when no other rule matches.
The rest of this tutorial will show you how to manage your policy. You can change the subscription policies and default policy through the RequestPolicy preferences.
Toolbar Icon
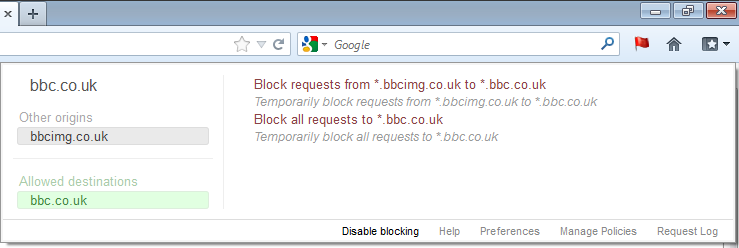
Once RequestPolicy is installed, you will see a new flag icon at the top-right of your browser window.
This flag turns red when RequestPolicy has blocked requests from the current website you are viewing.
Menu
Clicking on the RequestPolicy icon brings up a menu of options. Each destination domain that RequestPolicy has allowed or blocked requests to is listed on the left side of the menu. If a destination had some requests to it blocked and others allowed, it would be listed under another category called "Mixed destinations".
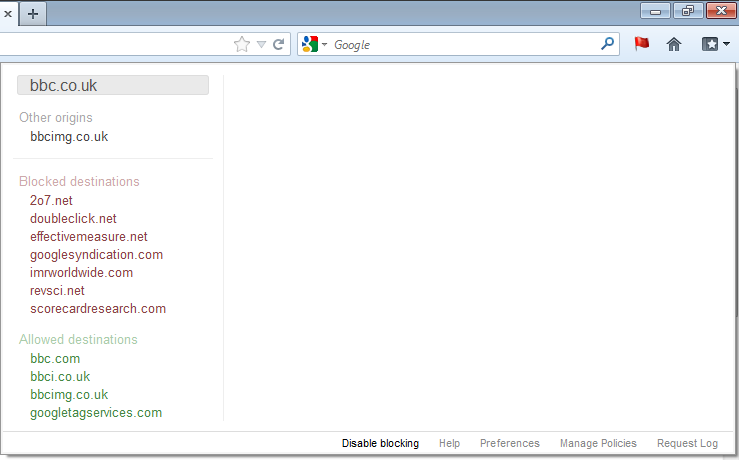
Blocked Destinations
If you click on one of the blocked destinations, you are shown options for changing which requests are blocked or allowed.
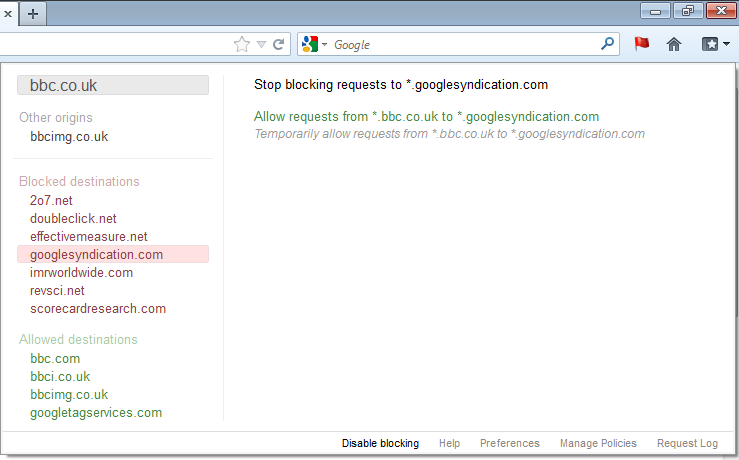
Allowed Destinations
You are shown similar options if you click on an allowed destination.
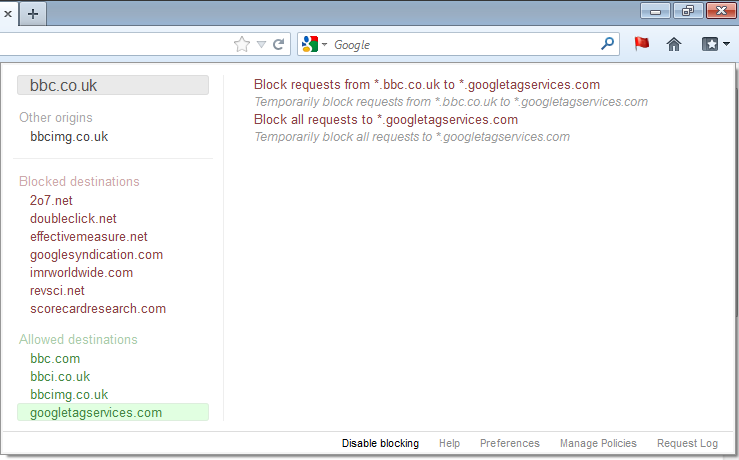
Other Origins
It's also possible that one of the destinations from this page was itself a document or redirect to some other destination. In that case, the destination is also an origin of requests and you'll see it listed under "Other origins". If you click on one of the other origins, the list of blocked and allowed destinations will change to show you the destinations from that origin.